Robust Meta-learning for Mixed Linear Regression with Small Batches
Published at Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2020
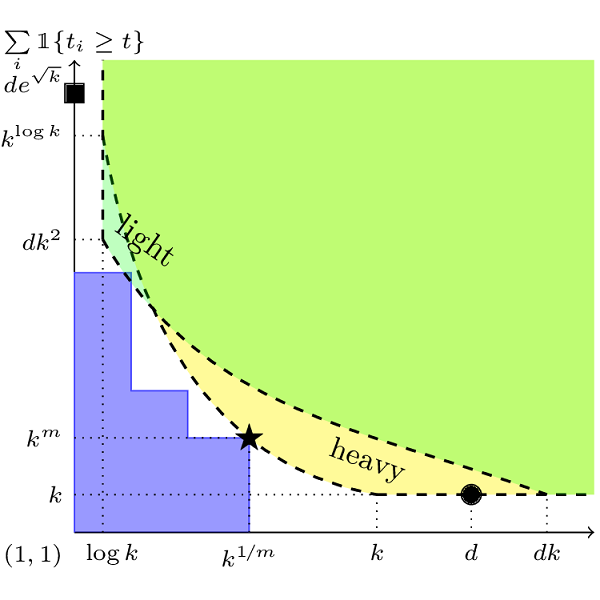
A common challenge faced in practical supervised learning, such as medical image processing and robotic interactions, is that there are plenty of tasks but each task cannot afford to collect enough labeled examples to be learned in isolation. However, by exploiting the similarities across those tasks, one can hope to overcome such data scarcity. Under a canonical scenario where each task is drawn from a mixture of \(k\) linear regressions, we study a fundamental question: can abundant small-data tasks compensate for the lack of big-data tasks? Existing second moment based approaches of Kong et al. (2020) show that such a trade-off is efficiently achievable, with the help of medium-sized tasks with \(\Omega(k^{1/2})\) examples each. However, this algorithm is brittle in two important scenarios. The predictions can be arbitrarily bad \((i)\) even with only a few outliers in the dataset; or \((ii)\) even if the medium-sized tasks are slightly smaller with \(o(k^{1/2})\) examples each. We introduce a spectral approach that is simultaneously robust under both scenarios. To this end, we first design a novel outlier-robust principal component analysis algorithm that achieves an optimal accuracy. This is followed by a sum-of-squares algorithm to exploit the information from higher order moments. Together, this approach is robust against outliers and achieves a graceful statistical trade-off; the lack of \(\Omega(k^{1/2})\)-size tasks can be compensated for with smaller tasks, which can now be as small as \({\cal O}(\log k)\).
The paper has been accepted at the NeurIPS 2020.
Please find the below resources:


Leave a Comment